Chinolone
Chinolone oder Oxochinoline sind Chinoline, die eine Carbonylgruppe an einer beliebigen Position des Chinolingerüsts tragen. Beispiele sind 2-Chinolon und 4-Chinolon.
-
.svg.png) Chinolin
Chinolin -
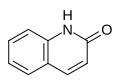 2-Chinolon
2-Chinolon -
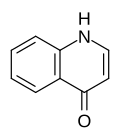 4-Chinolon
4-Chinolon
Chinolone sind eine unter pharmakologischen Aspekten bedeutsame Gruppe. Besonders bekannt sind die Chinolon-Antibiotika (meist kurz ebenfalls „Chinolone“ genannt), Abkömmlinge des 4-Chinolons mit antibiotischer Wirkung („Gyrasehemmer“). Darüber hinaus kommt die Chinolon-Teilstruktur auch in anderen pharmakologischen Wirkstoffen wie beispielsweise antiviralen und antiparasitären Mitteln oder Antineoplastika und Immunsuppressiva vor.[1]
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Maria L. S. Cristiano: Quinolones in Medicinal Chemistry: are Potential Applications Compromised by Limited Synthetic Approaches?. In: Organic and Medicinal Chemistry International Journal. 2017, Band 4, Nummer 5. doi:10.19080/OMCIJ.2017.04.555647.